In today’s digital world, privacy, security, and performance are of utmost importance. Many individuals and businesses rely on two popular services for these needs: VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VPN (Virtual Private Network).
At first glance, the abbreviations might seem interchangeable, but these services are distinctly different in their functions and applications.
This article will unravel the mystery behind VPS vs. VPN, so readers can make an informed decision on which solution is right for their needs.
Table of Contents
VPS vs. VPN – Understanding the Buzzwords
The first step in understanding the difference between VPN and VPS is to define each of these services and how they work. While both are designed to provide users with enhanced privacy, security, and performance, their applications and use cases vary significantly.
In the following sections, we’ll delve into the definitions, uses, advantages, and disadvantages of VPS and VPN and explore the key factors to consider when deciding which service is right for you.
What is a VPS?
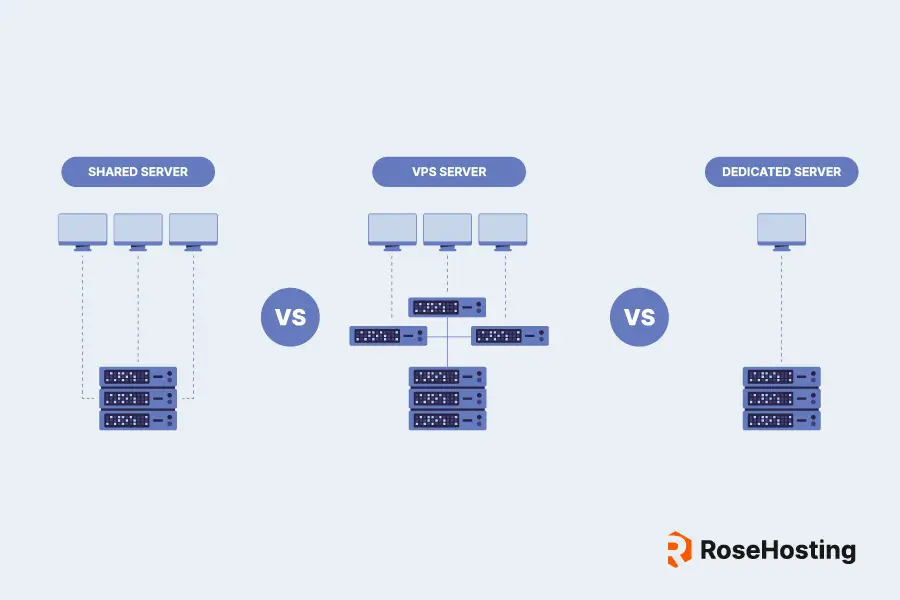
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a virtualized computing environment that simulates the functionality of a dedicated server while running on a shared physical hardware infrastructure. It is a type of web hosting solution that offers the benefits of both shared and dedicated server hosting.
VPS is created by partitioning a physical server into multiple isolated virtual machines (VMs) using virtualization technology. Each VM runs its own operating system (OS) and functions independently from the others, offering users more control, flexibility, and scalability than traditional shared hosting.
The virtualization technology used in VPS hosting is based on a hypervisor, which is a software layer that allows multiple VMs to run concurrently on a single physical server. The hypervisor allocates resources, such as CPU, memory, storage, and network bandwidth, to each VM based on predefined configurations. This ensures that each VM has dedicated resources, preventing one VM from affecting the performance of others.
Consequently, VPS hosting provides a more stable and reliable hosting environment when compared to shared hosting.
In a VPS hosting environment, users have full root access to their virtual server, allowing them to install and configure any software compatible with the chosen OS. This level of control is similar to having a dedicated server but at a lower cost.
VPS hosting is an ideal solution for users who require more resources and control than shared hosting can offer but do not want to invest in the cost and complexities associated with dedicated server hosting.
VPS hosting is typically offered in two main types: managed and unmanaged. In a managed VPS hosting plan, the hosting provider takes care of server maintenance, security updates, and other necessary tasks, allowing users to focus on their website or application.
Unmanaged VPS hosting, on the other hand, requires users to manage their server themselves, including handling software installation, updates, and troubleshooting. This option is suitable for users with technical expertise or those who prefer to have complete control over their server environment.
What is a VPN?
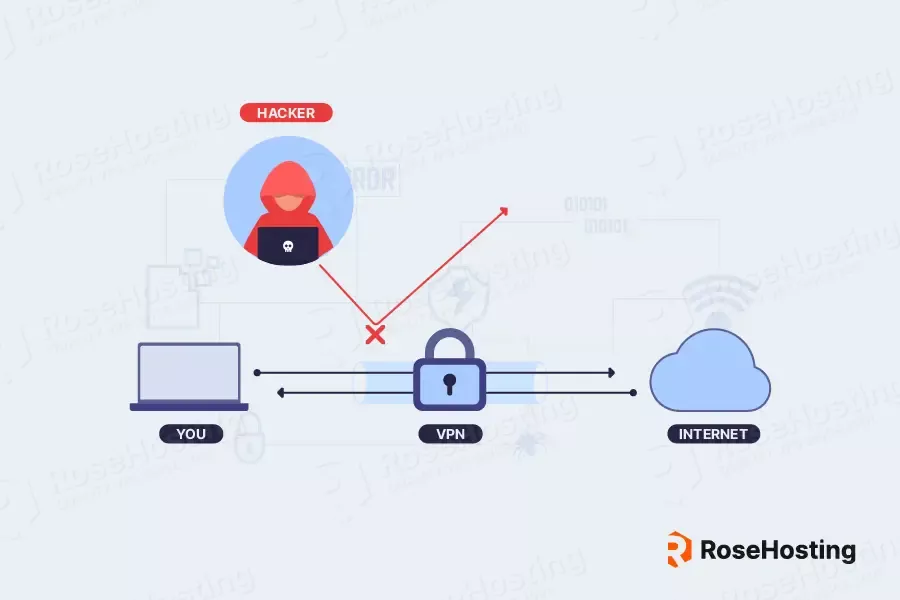
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that establishes a secure, encrypted connection between a user’s device and a remote server over the Internet.
It is designed to protect the user’s online privacy, enhance security, and bypass geographical restrictions on content access. This technology is widely used by individuals, businesses, and organizations to safeguard their online activities and maintain confidentiality.
The primary function of a VPN is to create a secure tunnel between the user’s device and the VPN server. This tunnel is established using advanced encryption protocols that secure the data transmitted between the device and the server. As a result, any data sent through this tunnel is protected from eavesdropping, hacking, and other potential online threats.
When a user connects to a VPN, their actual IP address is masked, and the VPN server assigns a new IP address to the user’s device. This new IP address is typically associated with the geographical location of the VPN server, which can be in a different country or region. As a result, the user’s online activity appears to originate from the VPN server’s location, effectively hiding their true location and identity.
In addition to enhanced security and privacy, VPNs also allow users to bypass content restrictions imposed by governments, ISPs, and content providers. For example, streaming services like Netflix and Hulu often have different content libraries for users in different countries due to licensing agreements.
By connecting to a VPN server in a specific country, users can gain access to the content library available in that region, bypassing geographical restrictions.
To use a VPN, a user needs to choose a VPN service provider and install the required VPN software on their device. The software establishes a connection to the VPN server, encrypts the data, and handles the entire process of maintaining a secure connection.
VPN service providers offer various features such as multiple server locations, different encryption protocols, and support for different devices and platforms.
Key Differences Between VPS and VPN
Now that we have a better understanding of what VPS and VPN are, it’s crucial to highlight the key differences between the two services.
- Purpose and Functionality: A VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a virtualized computing environment designed to provide users with dedicated resources and control over their hosting needs. It is primarily used for hosting websites, applications, and databases. On the other hand, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a secure and encrypted connection between users and the internet, used for enhancing online privacy, security, and bypassing geographic restrictions.
- Technical Implementation: VPS hosting involves dividing a physical server into multiple isolated virtual machines using virtualization technology. Each virtual machine runs its own operating system and functions independently from the others. In contrast, a VPN establishes a secure and encrypted “tunnel” between a user’s device and a remote VPN server. The user’s internet traffic is routed through this tunnel, effectively masking their IP address and encrypting their data.
- User Access and Control: With a VPS, users have root access to their virtual server and can install any software, configure system settings, and manage resources according to their needs. This level of control is not possible with a VPN. VPN users typically have access to a client application for connecting to the service, but they do not have control over the VPN servers or the underlying infrastructure.
- Target Audience: VPS hosting is targeted toward website owners, developers, and businesses that require more resources, control, and flexibility than shared hosting can offer. VPN services, on the other hand, cater to internet users looking for enhanced privacy, security, and the ability to bypass geo-restrictions on content.
- Pricing and Subscription Model: VPS hosting plans are generally billed monthly, and the cost depends on the resources allocated to the virtual server, such as CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth. VPN services offer subscription-based pricing, with options for monthly, annual, or multi-year plans. The pricing varies depending on the features, server locations, and the number of simultaneous connections allowed.
- Security and Privacy: While a VPS provides users with dedicated resources and control, it does not inherently offer enhanced security or privacy. Users are responsible for securing their VPS and the data stored on it. VPNs, however, are specifically designed to protect user data by encrypting internet traffic and masking the user’s IP address, making it difficult for third parties to track, intercept, or decipher their online activities.
VPS and VPN are two distinct technologies with different purposes and functionalities. While a VPS provides a virtualized computing environment for hosting websites and applications, a VPN secures and encrypts internet connections for enhanced privacy and security. Understanding the key differences between the two is essential when deciding which service is best suited to your needs.
VPS Advantages and Disadvantages
When considering whether a VPS is the right solution for your needs, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Greater control and customization: A VPS allows users to configure their server settings and install custom software, providing a higher level of flexibility compared to shared hosting.
- Improved performance: With dedicated resources and an isolated environment, VPS hosting can significantly improve the performance of websites and applications.
- Scalability: Users can easily upgrade or downgrade their server resources as their needs change, making VPS a more flexible solution than shared hosting.
Disadvantages
- Increased cost: While VPS hosting is more affordable than dedicated hosting, it’s still more expensive than shared hosting.
- Technical knowledge required: Managing a VPS requires a certain level of technical expertise, which may be a barrier for some users.
- Limited resources: Although VPS users have dedicated resources, they are still limited by the physical server’s capabilities.
VPN Advantages and Disadvantages
Similarly, evaluating the pros and cons of VPNs can help determine if this service is the right fit for your needs.
Advantages
- Enhanced privacy and security: VPNs encrypt user data and mask IP addresses, ensuring secure and anonymous internet access.
- Bypass geo-restrictions: VPNs allow users to access blocked content by connecting to servers in different countries.
- Improved network performance: By reducing latency and increasing bandwidth, VPNs can enhance the overall network performance.
Disadvantages
- Slower connection speeds: VPN encryption and routing can sometimes result in slower internet connection speeds.
- Compatibility issues: Some devices or applications may not be compatible with VPN services or may require additional configuration.
- Legal and ethical considerations: VPNs can be used for nefarious purposes, and some countries have strict regulations on their use.
Choosing the Right Solution: VPS or VPN?
When deciding between a VPS and a VPN, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and requirements. If you’re looking for a hosting solution that offers more control, customization, and scalability than shared hosting, a VPS may be the right choice for you.
On the other hand, if you’re seeking a service that provides enhanced privacy, security, and the ability to access blocked content, a VPN is the more suitable option.
VPS and VPN Use Cases and Applications
Understanding the various use cases and applications for VPS and VPN services can help further clarify which solution is right for your needs.
VPS Use Cases
- Web hosting: A VPS is an ideal solution for hosting websites that require more resources and customization than shared hosting can provide.
- Application hosting: VPS hosting can be used to host applications, such as e-commerce platforms or content management systems, that require dedicated resources and custom configurations.
- Virtual desktops: Users can create virtual desktop environments on a VPS, allowing them to access and manage their desktops from any device with an internet connection.
VPN Use Cases
- Secure browsing: VPNs ensure privacy and security while browsing the internet, protecting users from hackers, cybercriminals, and government surveillance.
- Accessing blocked content: VPNs enable users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content that would otherwise be blocked in their location.
- Remote access: Businesses can use VPNs to provide remote workers with secure access to their corporate networks.
Factors to Consider When Deciding Between VPS and VPN
When weighing the pros and cons of VPS and VPN services, consider the following factors to make an informed decision:
- Functionality: Determine whether you require a hosting solution (VPS) or a secure and private internet access solution (VPN).
- Privacy and security: If online privacy and security are your primary concerns, a VPN is the better choice.
- Scalability and customization: If you need a hosting solution with greater scalability and customization options, a VPS is a more suitable option.
- Cost: Consider your budget and the costs associated with each service, keeping in mind that VPS hosting is generally more expensive than VPN services.
- Technical expertise: Evaluate your technical skills and whether you’re comfortable managing a VPS, as it requires more technical knowledge than using a VPN.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between VPS and VPN, as well as their respective advantages and disadvantages, will help you make an informed decision on which service best meets your needs.
Whether you require a flexible and scalable hosting solution or a secure and private internet access service, both VPS and VPN offer valuable benefits to enhance your digital experience.
By considering your specific requirements and the factors outlined in this article, you can confidently choose the right solution for your needs.