Horizontal scaling is a method of adding numerous servers to a cluster to boost performance and offer high availability. The biggest advantage of horizontal scaling is that it provides room for growth and increases capacity on the fly.

But then again, the application must be meticulously designed to be able to sync well on all instances within the cloud.
Here’s all you need to know about the characteristics and benefits of horizontal scaling:
Table of Contents
What is the need for Horizontal Scaling?
When your application is in high demand and you are looking to scale your app’s availability, power and accessibility, do you actually scale-out or scale-up? Meaning, whether you need vertical scaling or horizontal scaling?
The real difference lies in the way you add computing resources to your business’s IT infrastructure. When you scale up viz. vertical scaling, you will be adding more power to your already existing machine. On the other hand, when you scale out viz. horizontal scaling, you will add more machines to your network to get additional resources into the system in order to share the memory workload and processing across various devices.
Why Horizontal Scaling is better than Vertical Scaling?
Scaling out (horizontal scaling) is a much better option than scaling up (vertical scaling), as your business won’t face any resource deficit.
Simply adding more power to your server might create bottlenecks, especially when it is taken offline for upgrades. What will you do if there is a sudden traffic spike and you have to upgrade the server again? Hence with vertical scaling, you will be limited in terms of “scaling up” to solve such problems.
Horizontal scaling, on the other hand, does not cause any resource deficit whatsoever. Businesses do not have to take their server offline while scaling out as this approach adds more resources to the existing ones. Horizontal scaling allows better elasticity than vertical scaling.
A few benefits of horizontal scaling are as follows:
- Costs as per the use
- Inbuilt redundancy
- High and continuous availability
- No limits to hardware capacity
- Allows easy sizing and resizing as per your requirements
- No need to pay for peak demand
Preferable Scaling Mode
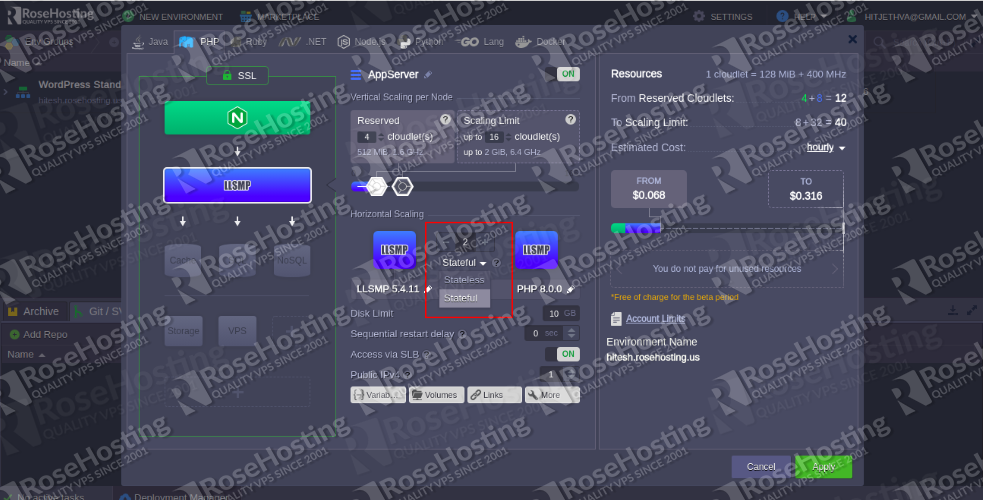
Horizontal scaling is a process of changing the number of nodes across a single layer. The preferable scaling mode for node groups can be selected when you create a new environment. Plus, you can use the topology wizard to adjust the scaling mode anytime for the existing one:
- Stateless: it will create all new nodes simultaneously from the base image template
- Stateful: it will sequentially copy the file system of the master container into the newly created nodes
Stateless scaling mode is faster, while the stateful scaling mode automatically copies the custom configurations such as custom SSL or deployments.
Migration to stateless apps is in continuous YOY growth
Stateless infrastructure creates an ideal business model implementation as it focuses on the application rather than the infrastructure. Such an approach is growing quite popular due to its “cool nature”, as it has become an industry standard to actually solve problems.
As per the Forrester reports, nearly 40% of enterprises across the world have already adopted a stateless approach, in some way or the other. The rest of them are still using stateful technologies along with the traditional deployment style, but are also planning to migrate to stateless technologies in the future.
Stateless vs Stateful applications
Stateful and stateless are two scaling modes through which applications are designed to either store or not store the “state”. This is later used for processing the requests.
Applications that store data from one request to another, and then use it to run later are known as stateful. For example, a stateful application will save a client’s information locally or on a remote host and then use this data later when the client makes a request. When the client puts up a request, it will be set as a variable that changes the server’s state. This change is stored in the memory, so if someone else tries to put up a request from another server with the same credentials, the connection fails as the second server does not have the right variable stored.
Scaling horizontally in this circumstance is almost impossible.
- Characteristics of stateless applications
A stateless application is an app that does not continuously interact between requests. An entire session (a series of interactions taking place between two requests) is not stored in the memory of the application.
A stateless application will not store data in a previous session to use it later in the upcoming session. Thus, each session acts as if it is running for the first time.
Due to this approach, it doesn’t matter which server client uses to make requests, as it does not store any state. After login, the server will send ID token containing session information, which the user can use to interact with the database.
Stateless applications scale horizontally very easily as compared to stateful applications due to the fact that infrastructure allows adding as many computing resources as needed.
What makes your application stateless?
Stateless applications contain several microservices which can be easily scaled, and each one of them has a specific objective.
The best example of a stateless app is the authentication service. Its main goal is to authenticate credentials, verify them and send back an ID token used to accept requests.
With stateless applications, you can focus on applications and not on infrastructure, as the server is managed by cloud vendors. Such apps save costs or at least keep them under control as you only have to pay for the resources you use. This is better than having machines ready to scale and pay for them at all times.
Another benefit of stateless applications is that the infrastructure is portable and can also be decoupled. This simplifies the infrastructure, reduces cost and also boosts business productivity, operational efficiency and development velocity.
Moreover, dynamic and horizontal scaling are inbuilt features in stateless apps to make sure the server doesn’t crash no matter how high the traffic spike gets on the app.
How to achieve effective horizontal scaling?
To ensure your service is highly compatible with horizontal scaling, there are various crucial practices to keep in mind:
The very first step is to make your application stateless as much as you can on the server side. Your application depends upon server-side tracking to check what it’s doing currently, and that user session is inevitably limited to that specific server. If you store all session-related specifics on browser-side, that session can seamlessly pass through multiple servers. Thus, the biggest advantage of horizontal scaling is its ability to handle a single session or hundreds/thousands of single sessions across multiple servers interchangeably.
The second step is to ensure your application development has a service-oriented architecture. If your app features self-contained and interactive logical blocks, you will be able to scale each one of them individually as per your workload needs. Developing your app with independent caching, application, web, and database tiers is always better. This will result in cost savings- as with this microservice architecture you don’t have to scale up every component of your application.
You can follow the below steps to implement Horizontal Scaling Based On Triggers:
Step 1 – Login to RoseHosting Cloud and create an environment for your application. You should see the following page:
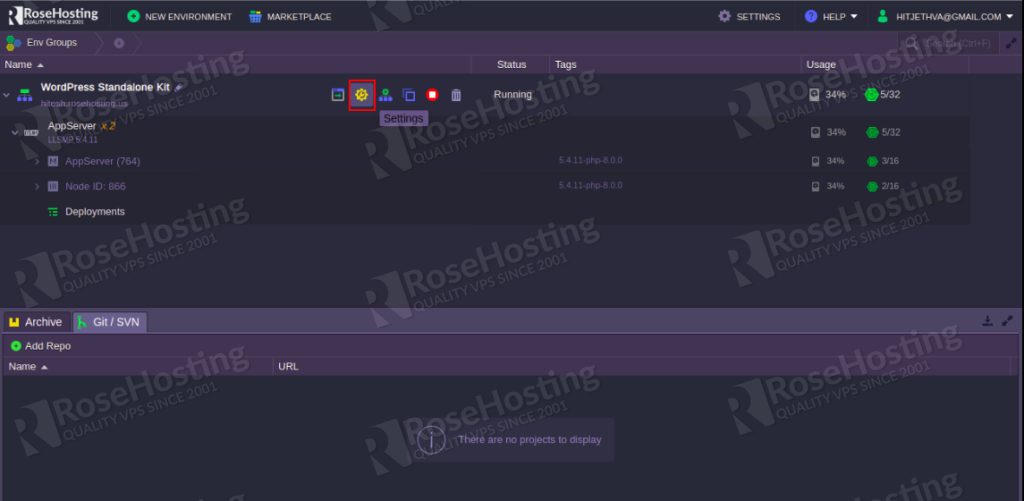
Click on the Settings button of your environment. You should see the following page:
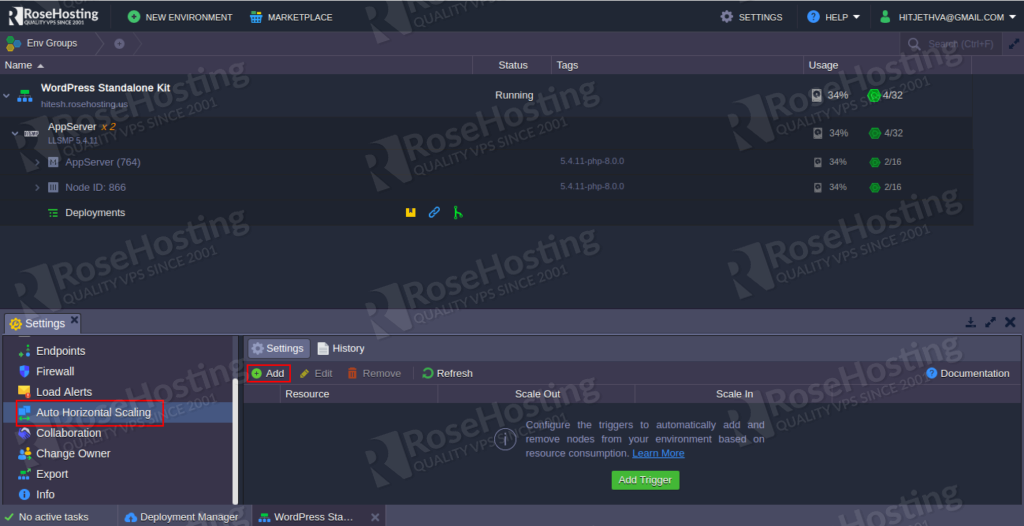
Step 2 – Click on the Auto Horizontal Scaling button in left pane, you should see the triggers for your environment in the right-side
Step 3 – Click on the ADD button to add a new triggers. You should see the following page:
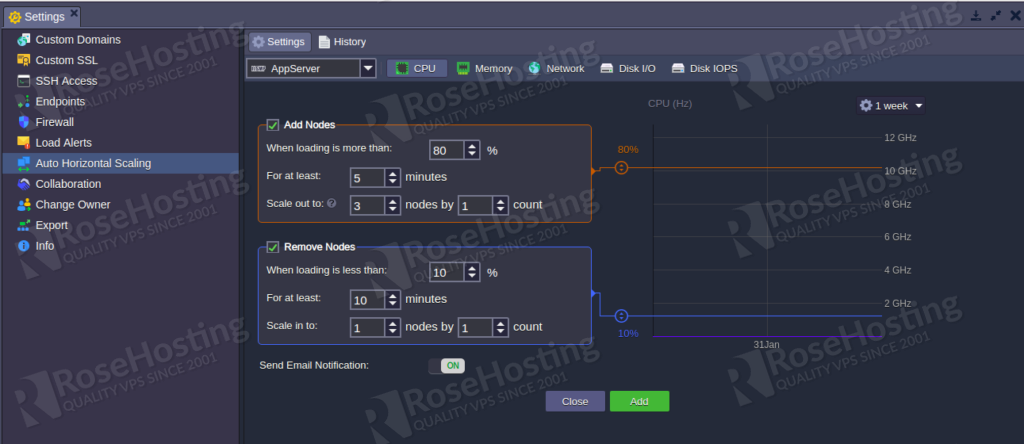
Step 4 – Set an add node and remove the node condition based on the load and also choose the resource type that you want to monitor. Then, click on the Add button to apply the changes.
When your server load is more or less than the trigger value which you have defined. You will receive an email notification. You can enable or disable the email notification using the button as shown below:
Wrap Up:

Since code is not tied up to any of the infrastructure components, stateless scaling model can scale horizontally and dynamically on-demand.
When building cloud-native applications that require an elastic and distributed environment, a stateless scaling model is the best. When developing a stateless app, make sure to consider factors like automation and orchestration, microservices architecture, and virtualization and containerization services.